-
News

Tamil Nadu Parties Differ on Special Intensive Revision of Electoral Rolls
Tamil Nadu Parties Differ on Special Intensive Revision of Electoral Rolls
Oct 30, 2025, 01:05 IST
Prashant Kishore’s explosive claim: Big ‘murder’ charge on deputy CM Samrat Choudhary; warns of legal action
Prashant Kishore’s explosive claim: Big ‘murder’ charge on deputy CM Samrat Choudhary; warns of legal action
Sep 30, 2025, 18:03 ISTParis Police Arrest Two Suspects in €88 Million Louvre Crown Jewels Heist
Paris Police Arrest Two Suspects in €88 Million Louvre Crown Jewels Heist
Oct 28, 2025, 17:58 IST
Justice D.Y. Chandrachud Reflects on Ayodhya Verdict and Gyanvapi Case
Justice D.Y. Chandrachud Reflects on Ayodhya Verdict and Gyanvapi Case
Sep 27, 2025, 16:10 IST
Trump Repeats India-Pakistan Peace Claim, Cites 250% Tariff Threat
Trump Repeats India-Pakistan Peace Claim, Cites 250% Tariff Threat
Oct 30, 2025, 01:32 IST
Studies Link 1.5 Million Annual Deaths in India to Air Pollution
More Than 17 Lakh Deaths in India Linked to Air Pollution in 2022: Lancet Report
Oct 30, 2025, 01:43 IST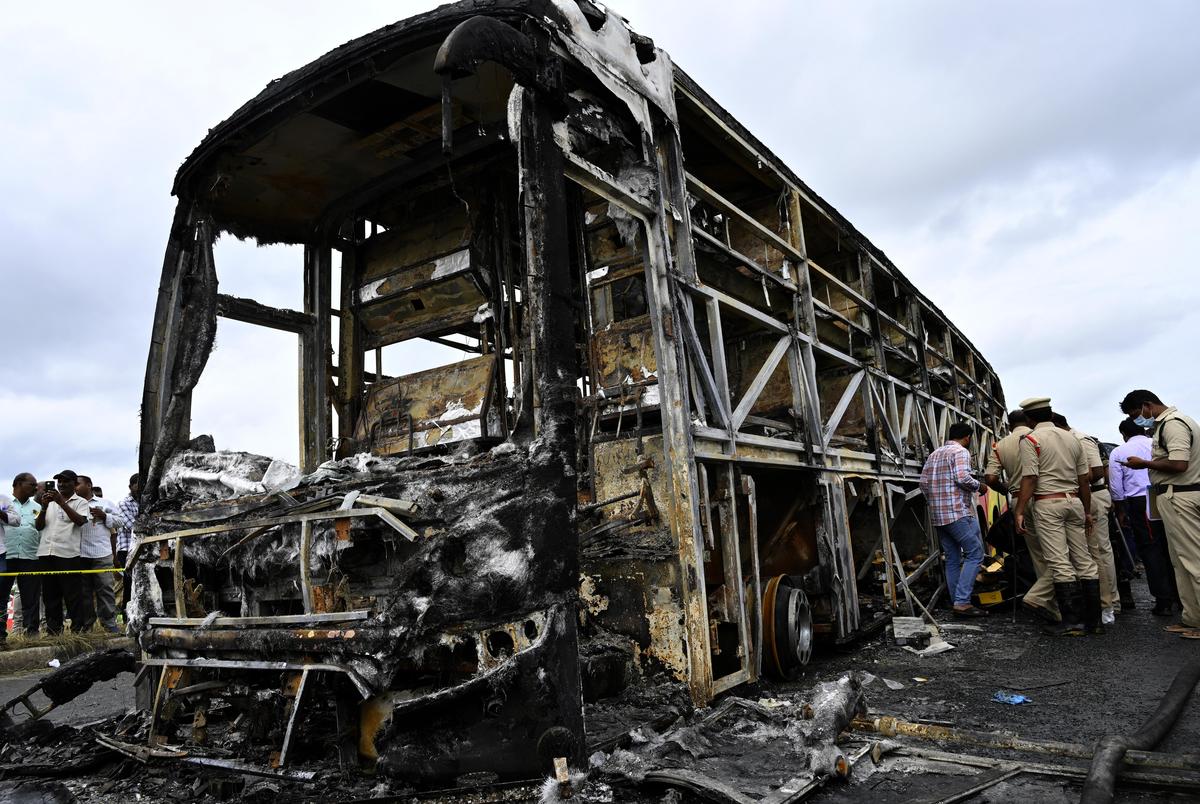
Tragic Bus Fire in Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh Claims 20 Lives, Sparks Nationwide Grief
Tragic Bus Fire in Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh Claims 20 Lives, Sparks Nationwide Grief
Oct 28, 2025, 12:46 IST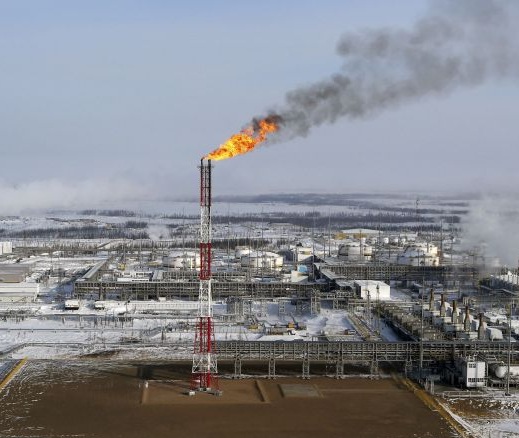
Ukraine’s Allies Tighten Oil Sanctions on Russia in Coordinated Push to Limit War Funding.
Ukraine’s Allies Tighten Oil Sanctions on Russia in Coordinated Push to Limit War Funding.
Oct 28, 2025, 11:51 IST -
World
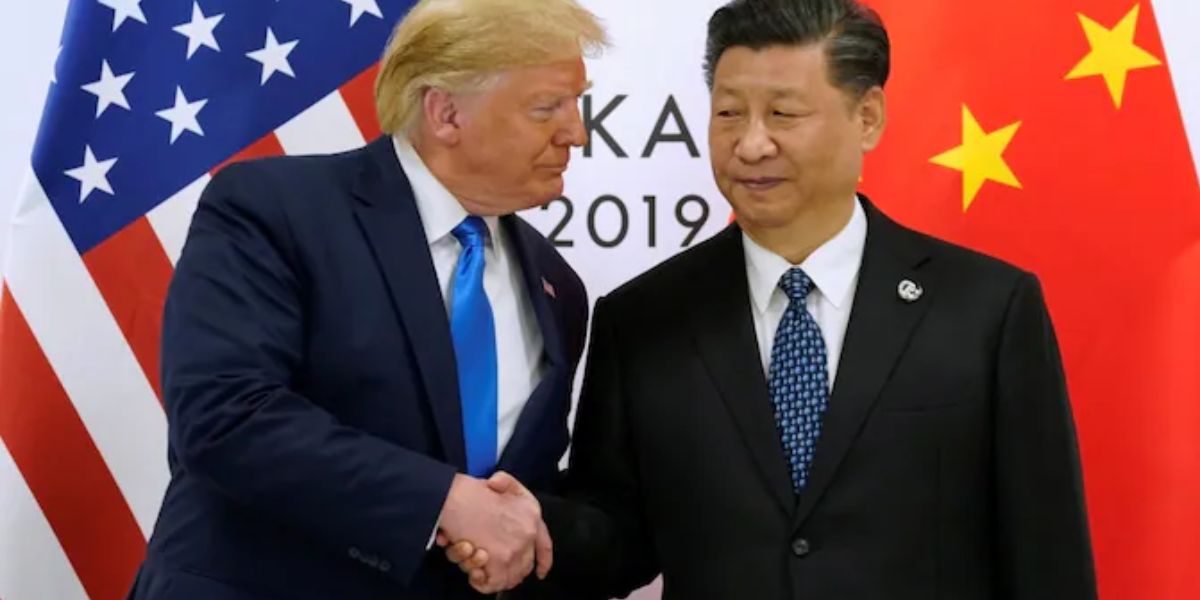

Trump, Xi Reach Trade Breakthrough: U.S. to Cut Tariffs on China
Trump, Xi Reach Trade Breakthrough: U.S. to Cut Tariffs on China
Oct 30, 2025, 15:31 IST
Saudi Arabia sets clear rules for Content Creators and Influencers: Everything you need to know
Saudi Arabia sets clear rules for Content Creators and Influencers: Everything you need to know
Sep 30, 2025, 19:58 IST -
Business

Budget 2025 income tax: Personal tax announcements from the Budget and their impact
Budget 2025 income tax: Personal tax announcements from the Budget and their impact
Oct 1, 2025, 15:53 ISTTrump Trade Deal Hopes Propel Indian Markets: Sensex Jumps 300 Points, Nifty Tests 26,050
Metal equities are leading the way as investors on Dalal Street feel better about the US-India trade deal.
Oct 29, 2025, 18:19 IST -
Startup
-
Sports

One-hour drama in Dubai: Inside details of how PCB chief Mohsin Naqvi ran away with Asia Cup trophy after India vs Pakis
One-hour drama in Dubai: Inside details of how PCB chief Mohsin Naqvi ran away with Asia Cup trophy after India vs Pakis
Sep 29, 2025, 11:10 IST
India Beat Pakistan by 5 Wickets, Refuse Asia Cup Trophy
India Beat Pakistan by 5 Wickets, Refuse Asia Cup Trophy
Sep 29, 2025, 10:46 IST
Kartik Tyagi’s 150kph Pace Powers Meerut into UP T20 Final
Kartik Tyagi’s 150kph Pace Powers Meerut into UP T20 Final
Sep 27, 2025, 16:02 IST
Suryakumar Yadav and Haris Rauf Fined 30% Match Fee by Officials
Suryakumar Yadav and Haris Rauf Fined 30% Match Fee by Officials
Sep 27, 2025, 15:37 IST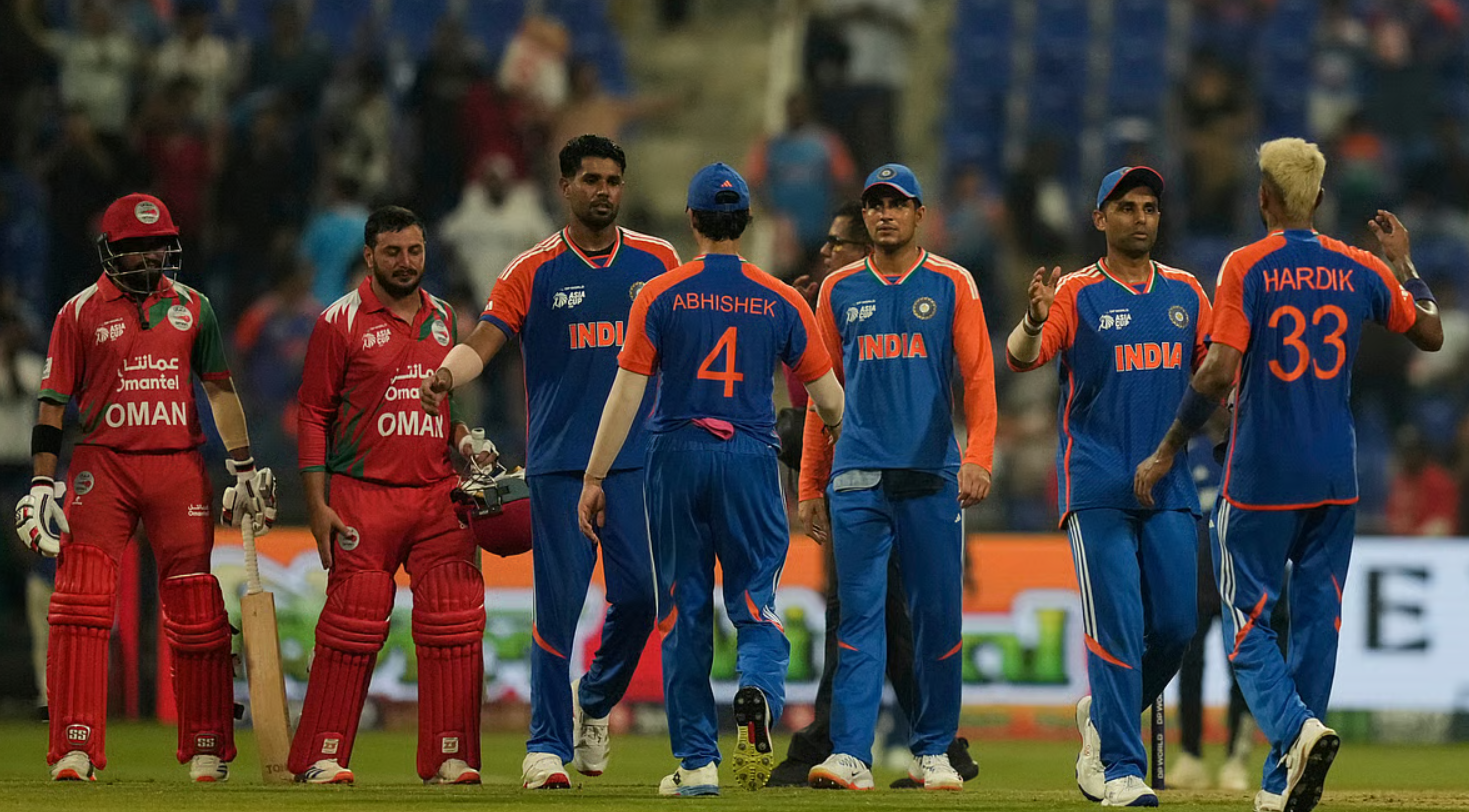
India Escapes Narrowly Against Oman: A Match of Unforeseen Twists
India Survives Oman Scare: A Match Defined by Resilience and Grit
Sep 20, 2025, 13:27 IST
Afghanistan's Spin Attack Poses Challenge for Bangladesh in Asia Cup
Asia Cup 2025: Afghanistan's Spin Attack Challenges Bangladesh's Top Order
Sep 16, 2025, 17:48 IST- FIFA World Cup
- UEFA Champions League
- English Premier League
- La Liga
- Serie A
- Bundesliga
- Indian Super League
- Copa América
- African Cup of Nations
- Euro Cup
- UEFA Europa League
- FIFA Club World Cup
- Transfer News
- Player Profiles
- Team Rankings
- Managerial Changes
- Match Highlights
- Historic Rivalries
- Stadium & Venue Updates

Tanzania Wins First-Ever Gold as Simbu Triumphs in Marathon
Sep 15, 2025, 18:48 IST -
Entertainment

'Aaryan’ Explores the Dark Side of Morality in a Crime-Driven Thriller
'Aaryan’ Explores the Dark Side of Morality in a Crime-Driven Thriller
Oct 30, 2025, 15:58 IST
The Bengal Files Opens with Strong Performances but Struggles with Emotional Impact
The Bengal Files Opens with Strong Performances but Struggles with Emotional Impact
Sep 29, 2025, 18:55 IST
Nishaanchi Movie Review: A Bold Entry into Gangster Drama
Nishaanchi Movie Review: A Bold Entry into Gangster Drama
Sep 26, 2025, 20:06 IST
Jolly LLB 3 Review: Courtroom Humor, Justice & Drama
Jolly LLB 3 Review: Courtroom Humor, Justice & Drama
Sep 20, 2025, 18:19 IST
Asrani, Iconic Comedy Legend of Indian Cinema, Passes Away at 84
Asrani, Iconic Comedy Legend of Indian Cinema, Passes Away at 84
Oct 21, 2025, 11:13 IST -
Lifestyle
-
Healthcare
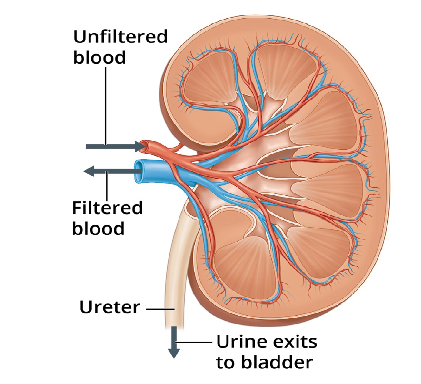
6 ‘healthy’ foods that may aggravate kidney stones
6 ‘healthy’ foods that may aggravate kidney stones
Oct 1, 2025, 16:18 IST -
Education

Gandhi Jayanti 2025: Speech and essay ideas for students
Gandhi Jayanti 2025: Speech and essay ideas for students
Oct 1, 2025, 16:33 IST
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
Markets showing resilience amid global uncertainty • Tech leaders call for AI regulation • Climate summit reaches historic agreement • New breakthrough in quantum computing announced • Sports: Championship final results
India vs England T20 World Cup 2025
‘Sikandar’ slowly inches toward Rs 110 crore in India
Leadership Strategies in a World of Uncertainty
Warmest April night in 3 years in Delhi, relief likely today







 Pakistan
Pakistan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Europe
Europe
 China
China
 Middle East
Middle East